Previous Chapter: AutoEncoder
Next Chapter: Recurrent Neural Network
Convolutional Neural Network
In machine learning, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a type of feed-forward artificial neural network in which the connectivity pattern between its neurons is inspired by the organization of the animal visual cortex. Individual neurons of the animal cortex are arranged in such a way that they respond to overlapping regions tiling the visual field, which can mathematically be described by a convolution operation. Convolutional networks were inspired by biological processes and are variations of multilayer perceptrons designed to use minimal amounts of preprocessing. They have wide applications in image and video recognition, recommender systems and natural language processing.
Following note is partially quoted from Standford Deep Learning Tutorial.
Note: Convolutional Neural Network(CNN)
Structure

Convolution
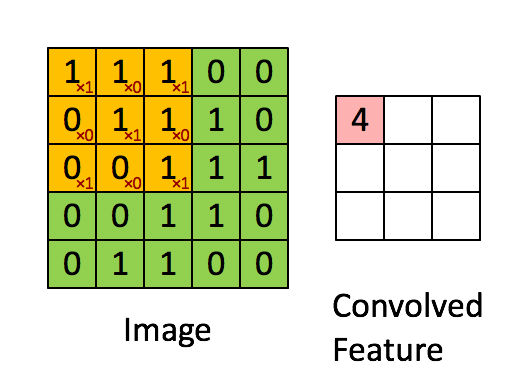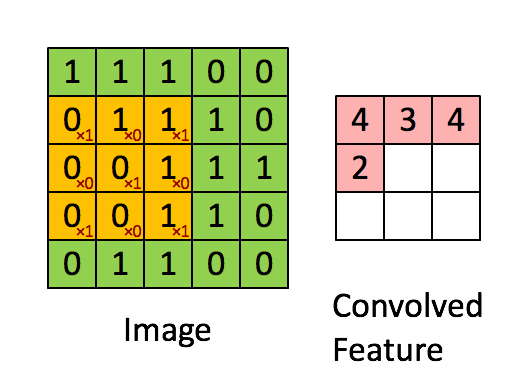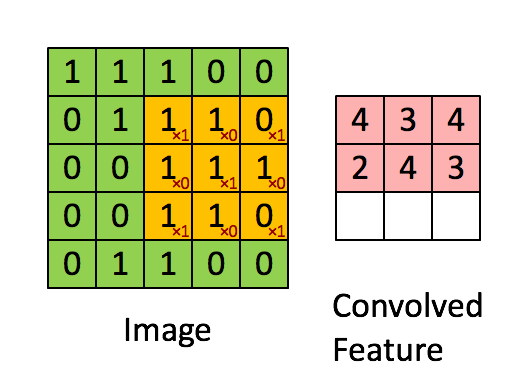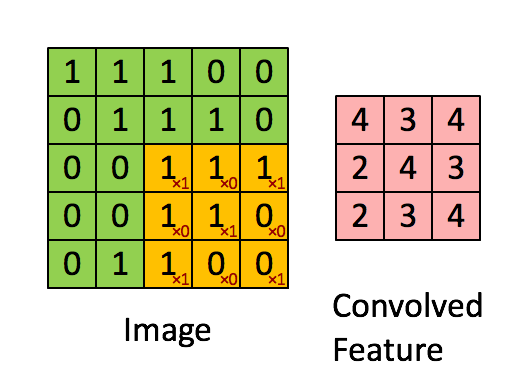
Since images have the ‘stationary’ property, which implies that features that are useful in one region are also likely to be useful for other regions. Thus, we use a rather small patch than the image size to convolve this image. For example, when having an image with m m r, we could use a n n q patch(where n < m && q <= r). The output will be produced in size m - n + 1.
 )
)
Pooling
To further reduce computation, pooling is introduced in CNN. As mentioned previously, a mean pooling is applied into each region of the image because of the ‘stationary’ property. Pooling usually ranges from 2 to 5.
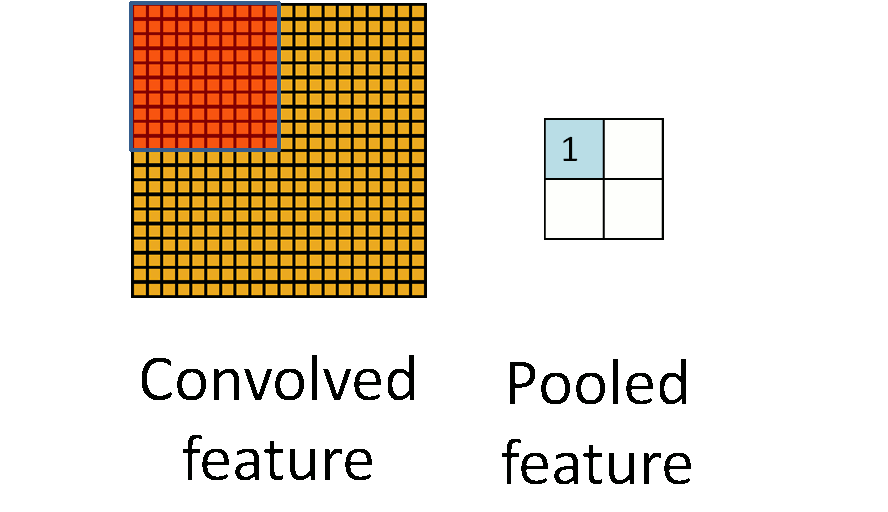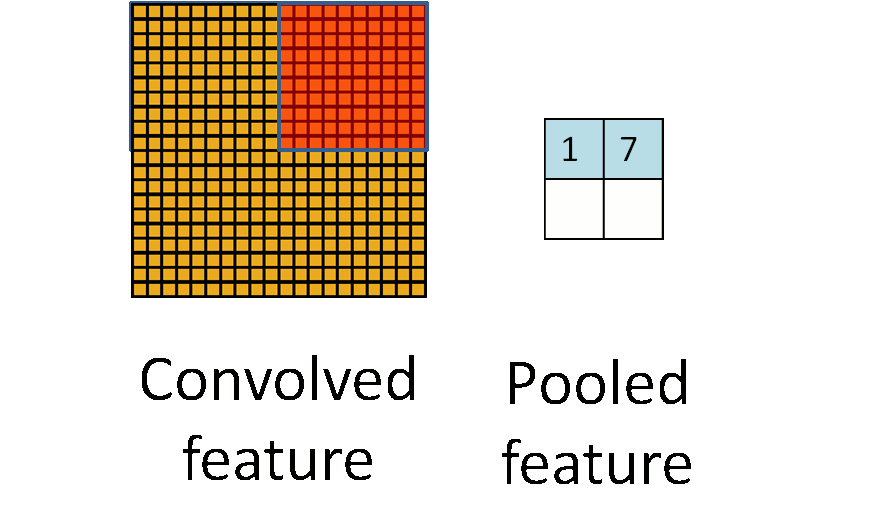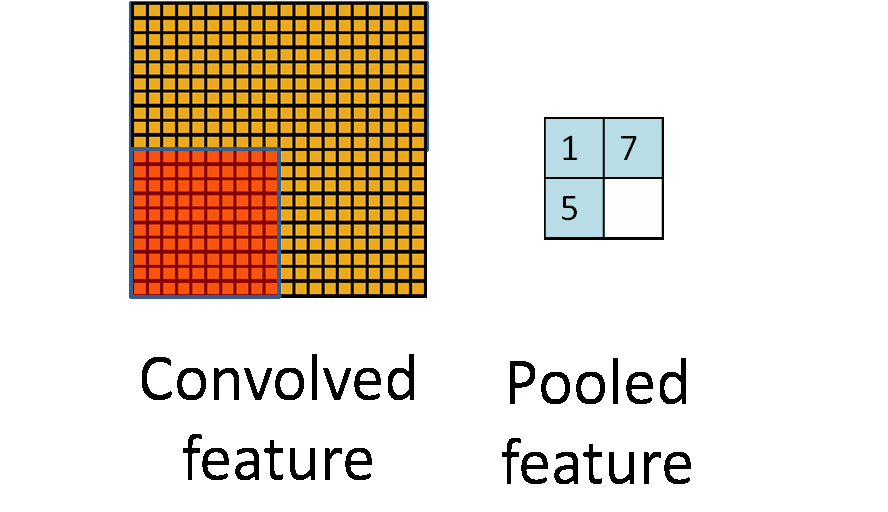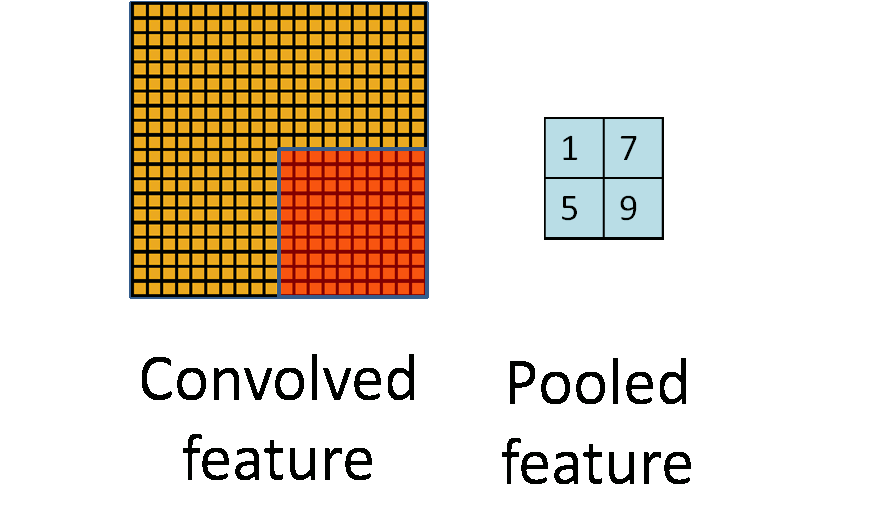 )
)
Others
- Densely Connected Layers: after several convolutional layers, a few densely conncetedly layers are usually constructed before the output layer;
- Top Layer Classifier: a top classifier is used to do supervised learning on CNN;
- Back Propogation: unsample on pooling layer and use the flipped filter on convolution layer;
Here is an exercise of building a Convolutional Neural Network using Tensorflow.
Exercise: Convolutional Neural Network
Necessary Header
|
|
MNIST data
|
|
Parameters
|
|
Inputs
|
|
Weights and Biases
|
|
Graph
In a traditional Convolutional Neural Network, we have several convolution layers and pool layers following by a fully-connected layer.
Covolutional Layer
|
|
Pool Layer
|
|
Model
|
|
Training Steps
|
|
Run a Session
|
|
Previous Chapter: AutoEncoder
Next Chapter: Recurrent Neural Network